A Complete Guide for Businesses
In today’s complex digital environment, traditional perimeter-based security models are no longer sufficient to protect organizations from evolving cyber threats. The rise of cloud adoption, remote work, and advanced cyberattacks has forced businesses to rethink how they secure their data and systems. One of the most effective strategies to emerge from this shift is Zero Trust Security—a framework built on the concept of “never trust, always verify.”
This article provides a deep dive into Zero Trust Security, its core principles, and why organizations of all sizes are implementing it to achieve comprehensive security in a borderless world.
What Is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity framework that assumes no assumed trust within or outside an organization’s network. Unlike traditional models where trust is automatically granted to users or devices inside the corporate perimeter, Zero Trust requires verification for every access request, no matter where it originates.
According to CrowdStrike, Zero Trust is based on the principle that every connection—whether it comes from employees, contractors, or third-party systems—must be verified and continuously monitored before being allowed access to resources.
This approach ensures attackers cannot exploit “trusted” internal networks, which are often the weakest link in legacy architectures.
Why Traditional Security Models Fall Short
Legacy security models rely on the idea that threats come from outside the network. Once users or devices pass perimeter defenses (like firewalls or VPNs), they are often granted broad access. This outdated model introduces major risks:
-
Insider threats remain unchecked.
-
Stolen credentials can move laterally without detection.
-
Cloud and remote work environments are left exposed.
As Microsoft explains, modern IT infrastructures no longer have defined boundaries. Organizations now operate in hybrid and multi-cloud environments, and employees access critical resources from anywhere in the world. Zero Trust solves these challenges by eliminating blind trust and enforcing continuous monitoring.

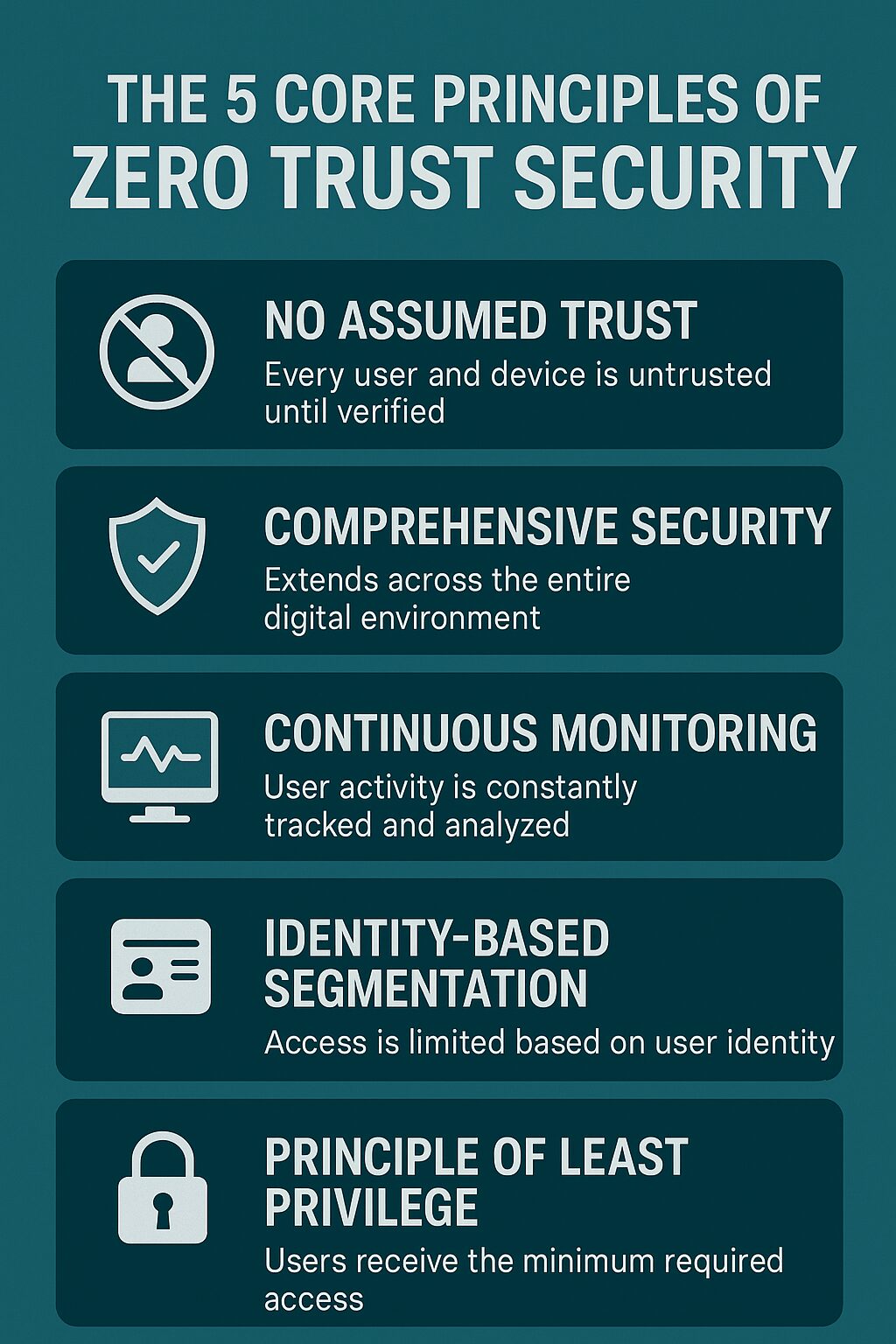
Core Principles of Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust is not a single product—it’s a security philosophy supported by specific practices and technologies. Key principles include:
1. No Assumed Trust
Every user, device, and application is treated as untrusted until verified. As Cloudflare highlights, this principle prevents attackers from exploiting “trusted” access inside networks.
2. Comprehensive Security Across All Environments
Zero Trust extends protection beyond the network perimeter to include endpoints, applications, and data. Whether workloads are in the cloud, on-premises, or hybrid, Zero Trust policies ensure comprehensive security across all touchpoints.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Validation
Verification doesn’t end after login. Zero Trust requires continuous monitoring of user behavior, device health, and network traffic. This allows real-time detection of anomalies and limits the potential damage of compromised accounts.
4. Identity-Based Segmentation
Rather than relying on static network zones, Zero Trust applies identity-based segmentation to limit access. Each user and device is only granted permissions necessary for their role, reducing attack surfaces and preventing lateral movement.
5. Principle of Least Privilege
At the heart of Zero Trust is the principle of least privilege. Users only get access to the minimum resources required to perform their duties. According to Palo Alto Networks, enforcing least privilege reduces exposure and limits the blast radius of potential breaches.
Benefits of Implementing Zero Trust Security
Adopting a Zero Trust model provides organizations with significant advantages:
-
Stronger protection against breaches: Even if attackers compromise credentials, segmentation and monitoring make it difficult to move laterally.
-
Adaptability to remote and hybrid work: Zero Trust supports secure access from any location or device.
-
Improved regulatory compliance: Identity and access management policies help meet data protection requirements.
-
Reduced insider threat risks: Strict access controls prevent employees from accessing unnecessary sensitive data.
-
Future-proof security: As IT environments evolve, Zero Trust adapts by focusing on identity and data instead of physical perimeters.
Zscaler notes that businesses embracing Zero Trust often see reduced operational costs associated with managing complex legacy infrastructure.
Key Technologies Enabling Zero Trust
Zero Trust Security is powered by a range of security tools and solutions, including:
-
Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Ensures user identity cannot be compromised by stolen passwords alone.
-
Endpoint detection and response (EDR): Monitors devices for suspicious activity.
-
Secure web gateways (SWG) and cloud access security brokers (CASB): Protect cloud applications and web traffic.
-
Identity and access management (IAM): Provides granular control over permissions and authentication.
-
Microsegmentation technologies: Isolate workloads and minimize the attack surface.
Organizations often combine these tools into a unified strategy, leveraging platforms offered by leaders such as Microsoft, Palo Alto Networks, and CrowdStrike.
Common Challenges in Zero Trust Adoption
While the benefits are clear, implementing Zero Trust Security can pose challenges:
-
Cultural shift: Teams accustomed to open access may resist stricter controls.
-
Complex integration: Legacy infrastructure may require significant updates.
-
Ongoing management: Zero Trust is not a “set it and forget it” model; it requires continuous adaptation.
-
Cost considerations: Upgrading to modern IAM and monitoring solutions can be expensive upfront.
However, the long-term value in preventing costly data breaches outweighs these hurdles for most organizations.
Best Practices for Zero Trust Implementation
To maximize success, organizations should:
- Start with identity: Ensure strong authentication and role-based access policies.
- Adopt least privilege early: Limit access to sensitive data and applications.
- Segment networks and workloads: Apply identity-based segmentation for tighter control.
- Invest in monitoring: Use behavioral analytics and continuous validation.
- Educate employees: Promote awareness of Zero Trust principles to build cultural alignment.
By phasing adoption and leveraging trusted vendors, organizations can steadily transition to a full Zero Trust architecture without disrupting business operations.
The Future of Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust Security is no longer a “nice-to-have”—it is quickly becoming the global standard for cybersecurity. As regulatory bodies and industry frameworks emphasize stronger access controls and monitoring, Zero Trust will play a central role in compliance strategies.
With vendors like Cloudflare, Zscaler, and CrowdStrike advancing the technology landscape, businesses now have powerful tools to accelerate their journey toward Zero Trust.
Final Thoughts
Zero Trust Security represents a paradigm shift from outdated perimeter-based defenses to a dynamic, identity-driven model designed for the realities of today’s cyber landscape. By eliminating assumed trust, enforcing continuous monitoring, leveraging identity-based segmentation, and applying the principle of least privilege, organizations can achieve comprehensive security that evolves with their needs.
For businesses serious about safeguarding data, employees, and customers, adopting a Zero Trust approach is no longer optional—it’s essential.